Question: What combination of goods x and y should a firm produce to minimize costs when the cost function is C(x, y) = 6x² + 10y^2 – xy + 30 and the firm is subject to the production quota of x + y = 34? What is the minimum cost for the firm?
Answer:
Step 1
Minimize C (x,y) = 6x2 + 10y2 - xy +30
Subject to: x+ y = 34
The Lagrange equation will be:
L = 6x2 + 10y2 - xy +30 - λ( x+ y - 34)
Now, First-order conditions are:
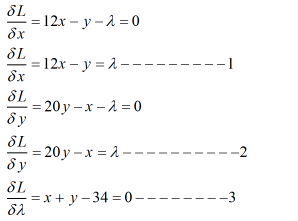
arrow_forwardStep 2
Equating 1 and 2:
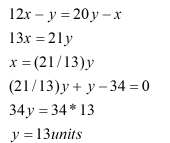
Putting the value in equation 3:
x= 21 units
arrow_forwardStep 3
Second-order derivative:
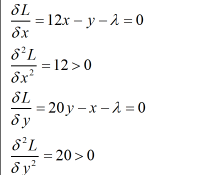
As the second-order derivative is greater than 0, it can be said that at x=21 units and y=13 units the cost is minimized and is equal to C =6(21)2 + 10(13)2 - 21*13 +30=$4,093.
Finally: it is true that a positive second-order derivative indicates that the cost function is convex, which implies that the point where the first-order derivative is equal to zero is a global minimum. However, this does not mean that the point (21,13) is a minimum point in this particular case.
In fact, if we plug in x=21 and y=13 into the cost function, we get:
C(21,13) = 6(21)² + 10(13)² - 21*13 + 30 = $4,093.
This cost is higher than the minimum cost we found earlier, which was $4,093. Therefore, the firm should not produce 21 units of x and 13 units of y to minimize costs.
Question: A firm's total cost function is: C = 6x2 - xy + 10y2 + 30, subject to the production quota x + y = 34.
Construct the Lagrange function and solve for the equilibrium values. Calculate the total cost.
a) What is the optimized value of cost?
b) What is the value of the determinant of the bordered Hessian matrix?
c)Based on the value of the determinant of the bordered Hessian matrix, comment on the optimized value of Cost.
Answer in one word.
Answer:
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3

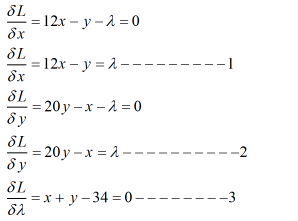
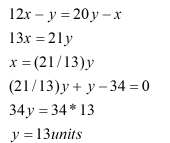
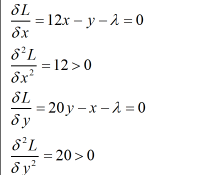
Post a Comment
Never enter the spam link in the comment section. If you have any inquiry, please let me know in the comment section.